Python Institue (PCEP) exercices
Some exercices from Python Essentials Part1
ref: https://edube.org/

Operators And Expressions
ref. https://edube.org/learn/pe-1/lab-operators-and-expressions-11
Estimated time
15-20 minutes Level of diffi.7culty
Easy Objectives
improving the ability to use numbers, operators, and arithmetic operations in Python;
using the print() function's formatting capabilities;
learning to express everyday-life phenomena in terms of programming language.
Scenario
Your task is to prepare a simple code able to evaluate the end time of a period of time, given as a number of minutes (it could be arbitrarily large). The start time is given as a pair of hours (0..23) and minutes (0..59). The result has to be printed to the console.
For example, if an event starts at 12:17 and lasts 59 minutes, it will end at 13:16.
Don’t worry about any imperfections in your code - it’s okay if it accepts an invalid time - the most important thing is that the code produce valid results for valid input data.
Test your code carefully. Hint: using the % operator may be the key to success.
CODE
hour = int(input("Starting time (hours): "))
mins = int(input("Starting time (minutes): "))
dura = int(input("Event duration (minutes): "))
time_hour = (hour+dura//60 + (mins+dura%60)//60)%24
time_min = (mins+dura%60)%60
print("It will end at " + str(time_hour) + ":" + str(time_min))
Break and Continue
ref. https://edube.org/learn/pe-1/lab-the-break-statement-stuck-in-a-loop-3
Estimated time
10-20 minutes Level of difficulty
Easy Objectives
Familiarize the student with:
using the break statement in loops;
reflecting real-life situations in computer code.
Scenario
The break statement is used to exit/terminate a loop.
Design a program that uses a while loop and continuously asks the user to enter a word unless the user enters “chupacabra” as the secret exit word, in which case the message “You’ve successfully left the loop.” should be printed to the screen, and the loop should terminate.
Don’t print any of the words entered by the user. Use the concept of conditional execution and the break statement.
q
secret = "chupacabra"
counter = 0
while True:
word = str(input("Enter a word: "))
if word == secret:
break
counter += 1
print("Looooooping.", counter)
print("You've successfully left the loop.")
The Continue Statement The Ugly Vowel Eater
ref. https://edube.org/learn/pe-1/lab-the-continue-statement-the-ugly-vowel-eater-3
Estimated time
10-20 minutes Level of difficulty
Easy Objectives
Familiarize the student with:
using the continue statement in loops;
reflecting real-life situations in computer code.
Scenario
The continue statement is used to skip the current block and move ahead to the next iteration, without executing the statements inside the loop.
It can be used with both the while and for loops.
Your task here is very special: you must design a vowel eater! Write a program that uses:
a for loop; the concept of conditional execution (if-elif-else) the continue statement.
Your program must:
Ask the user to enter a word;
Use user_word = user_word.upper() to convert the word entered by the user to upper case;
We’ll talk about the so-called string methods and the upper() method very soon - don’t worry;
Use conditional execution and the continue statement to “eat” the following vowels A, E, I, O, U from the inputted word; print the uneaten letters to the screen, each one of them on a separate line.
Test your program with the data we’ve provided for you.
Test data
Sample input: Gregory
Expected output:
GRGRY
Sample input: abstemious
Expected output:
BSTMS
Sample input: IOUEA
Expected output:
??
CODE
#!/bin/usr/env python3
word_without_vowels = ""
# Prompt the user to enter a word
# and assign it to the user_word variable.
user_word = str(input("Enter a Word:"))
user_word = user_word.upper()
for letter in user_word:
# Complete the body of the loop.
if letter == "A":
continue
elif letter == "E":
continue
elif letter == "I":
continue
elif letter == "O":
continue
elif letter == "U":
continue
else:
word_without_vowels += letter
# Print the word assigned to word_without_vowels.
print(word_without_vowels)
3.2.1.14 LAB: Essentials of the while loop
ref.: https://edube.org/learn/pe-1/lab-essentials-of-the-while-loop-3
Estimated time 20-30 minutes Level of difficulty Medium
Objectives
Familiarize the student with:
using the while loop;
finding the proper implementation of verbally defined rules;
reflecting real-life situations in computer code.
Scenario
Listen to this story: a boy and his father, a computer programmer, are playing with wooden blocks. They are building a pyramid.
Their pyramid is a bit weird, as it is actually a pyramid-shaped wall - it’s flat. The pyramid is stacked according to one simple principle: each lower layer contains one block more than the layer above.
The figure illustrates the rule used by the builders:
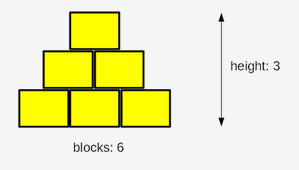
Your task is to write a program which reads the number of blocks the builders have, and outputs the height of the pyramid that can be built using these blocks.
Note: the height is measured by the number of fully completed layers - if the builders don’t have a sufficient number of blocks and cannot complete the next layer, they finish their work immediately.
Test your code using the data we’ve provided.
Test Data
Sample input: 6
Expected output: The height of the pyramid: 3
Sample input: 20
Expected output: The height of the pyramid: 5
Sample input: 1000
Expected output: The height of the pyramid: 44
Sample input: 2
Expected output: The height of the pyramid: 1
blocks = int(input("Enter the number of blocks: "))
#
# Write your code here.
#
height = 0
inlayer = 1
while inlayer <= blocks:
height += 1
blocks -= inlayer
print("blocks: ",blocks)
inlayer += 1
print("inlayer: ",inlayer)
print("The height of the pyramid:", height)
Enter the number of blocks: 6
blocks: 5
inlayer: 2
blocks: 3
inlayer: 3
blocks: 0
inlayer: 4
The height of the pyramid: 3